ROACHNEST Documentation¶
Copyright & Licensing¶
ROACHNEST: A browser based user interface for monitor & control of CASPER hardware
Copyright (C) 2011 Danny Price
Everything I’ve written: GNU General Public License (GPL)
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>
Everything else: As per author’s original licensing terms. Bottle.py and Flot are MIT licensed, Blueprint is a modified MIT license, sqlite3 is public domain.
Introduction¶
Roachnest is a browser based Graphical User Interface (GUI) for control of CASPER hardware. This script utilises the KATCP python libraries, the bottle web framework, and sqlite3:
The HTML/CSS is based on blueprint CSS web framework, and plotting is done with HTML5/javascript flot:
Warning: I strongly suggest that this is available only through an internal network and is not made accessible via the WWW. Use at your own risk.
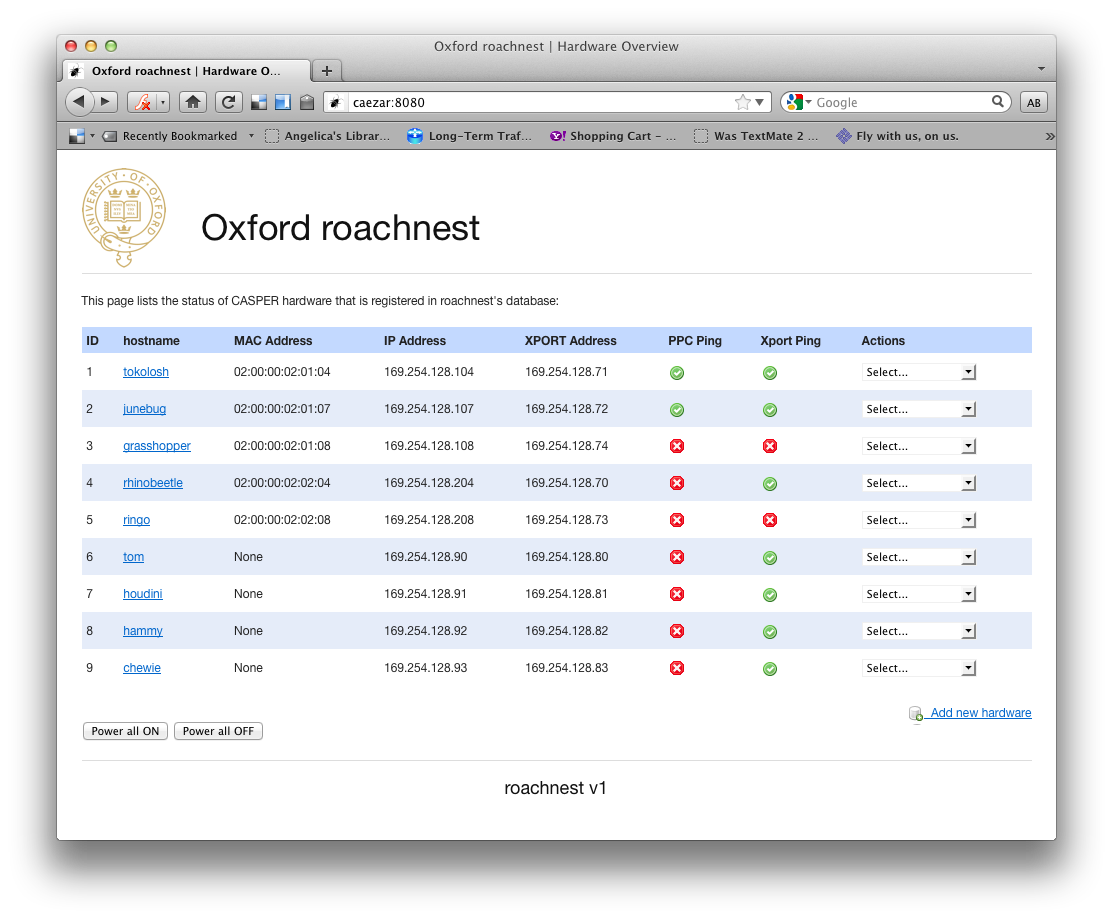
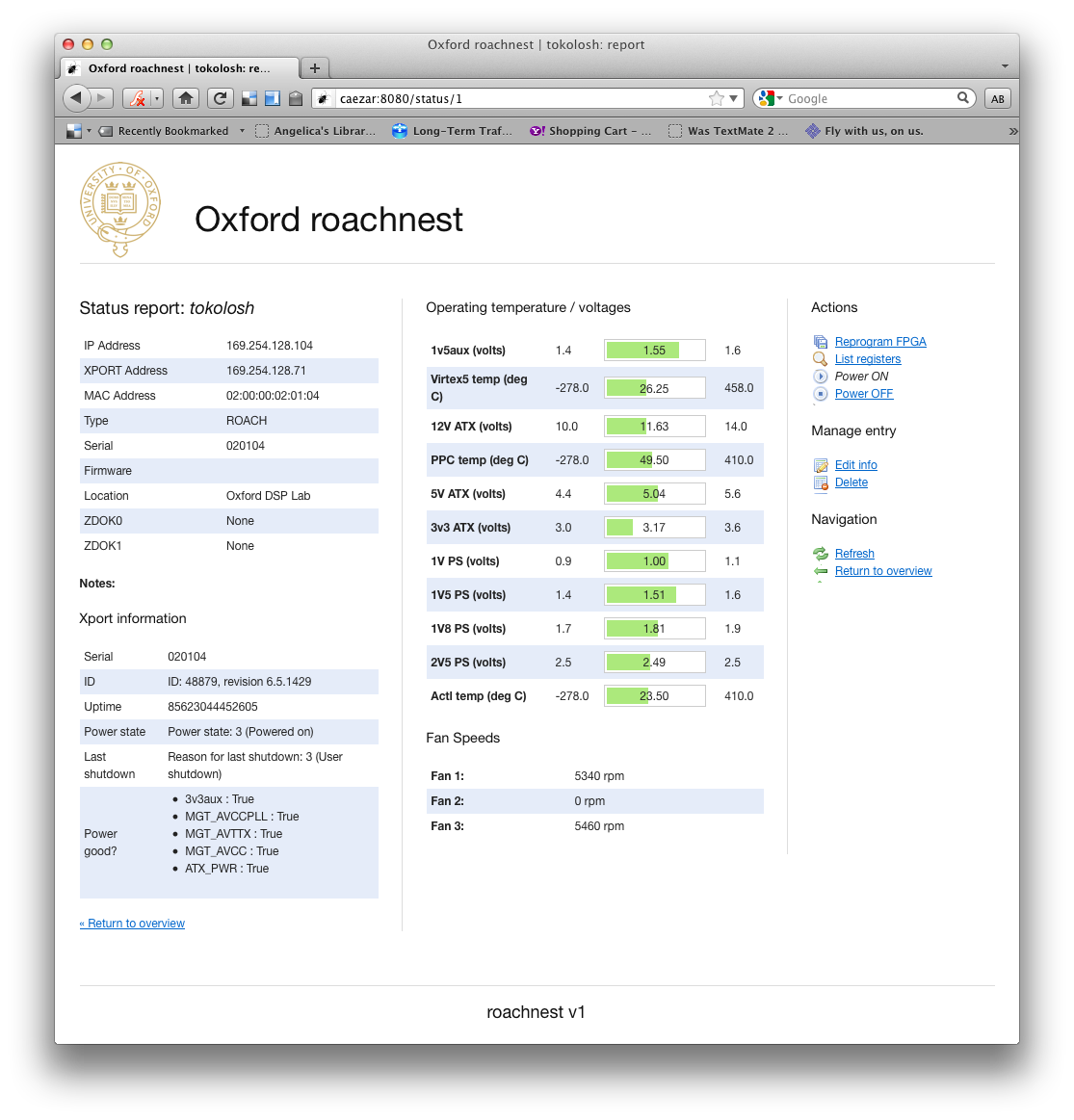
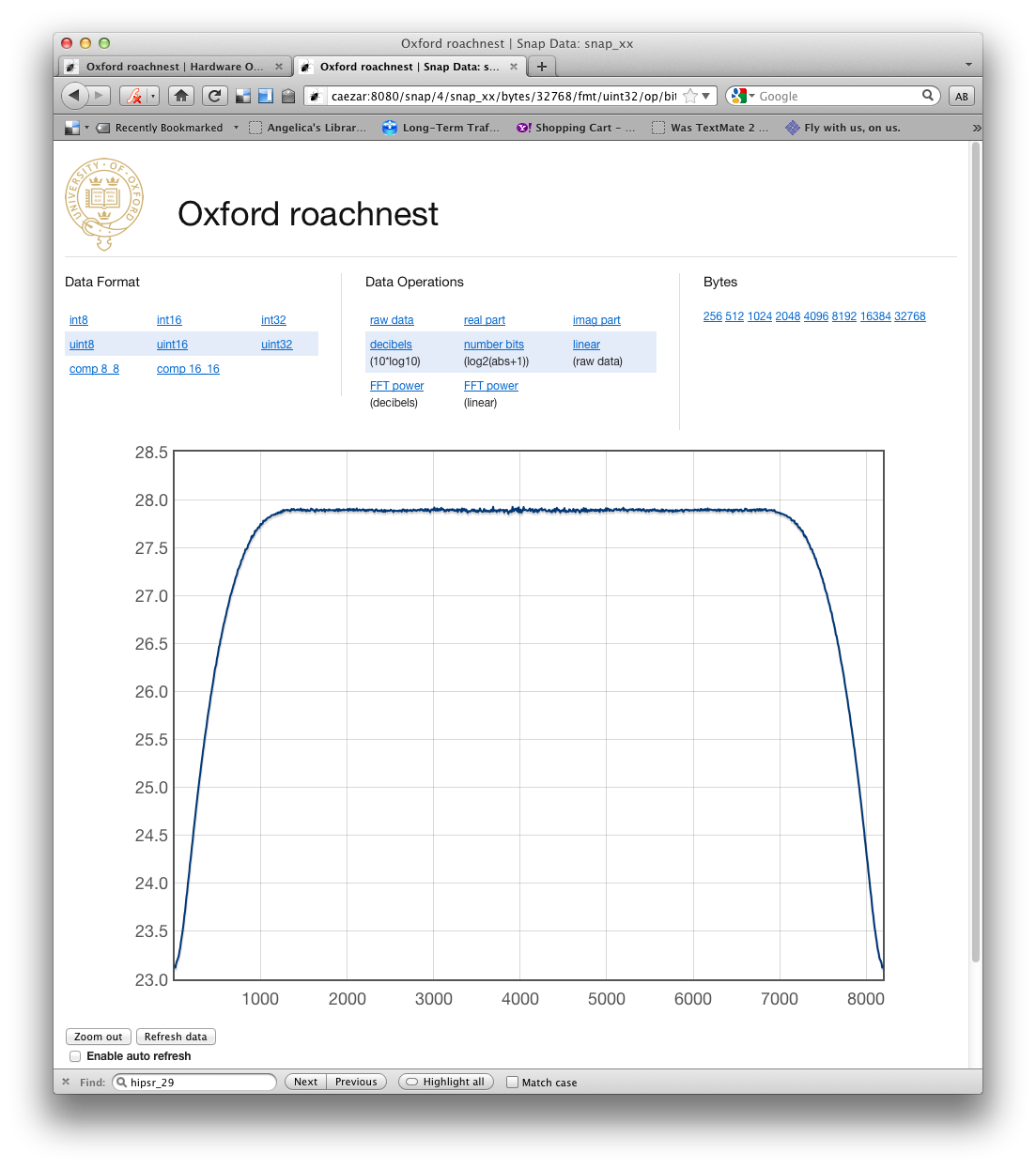
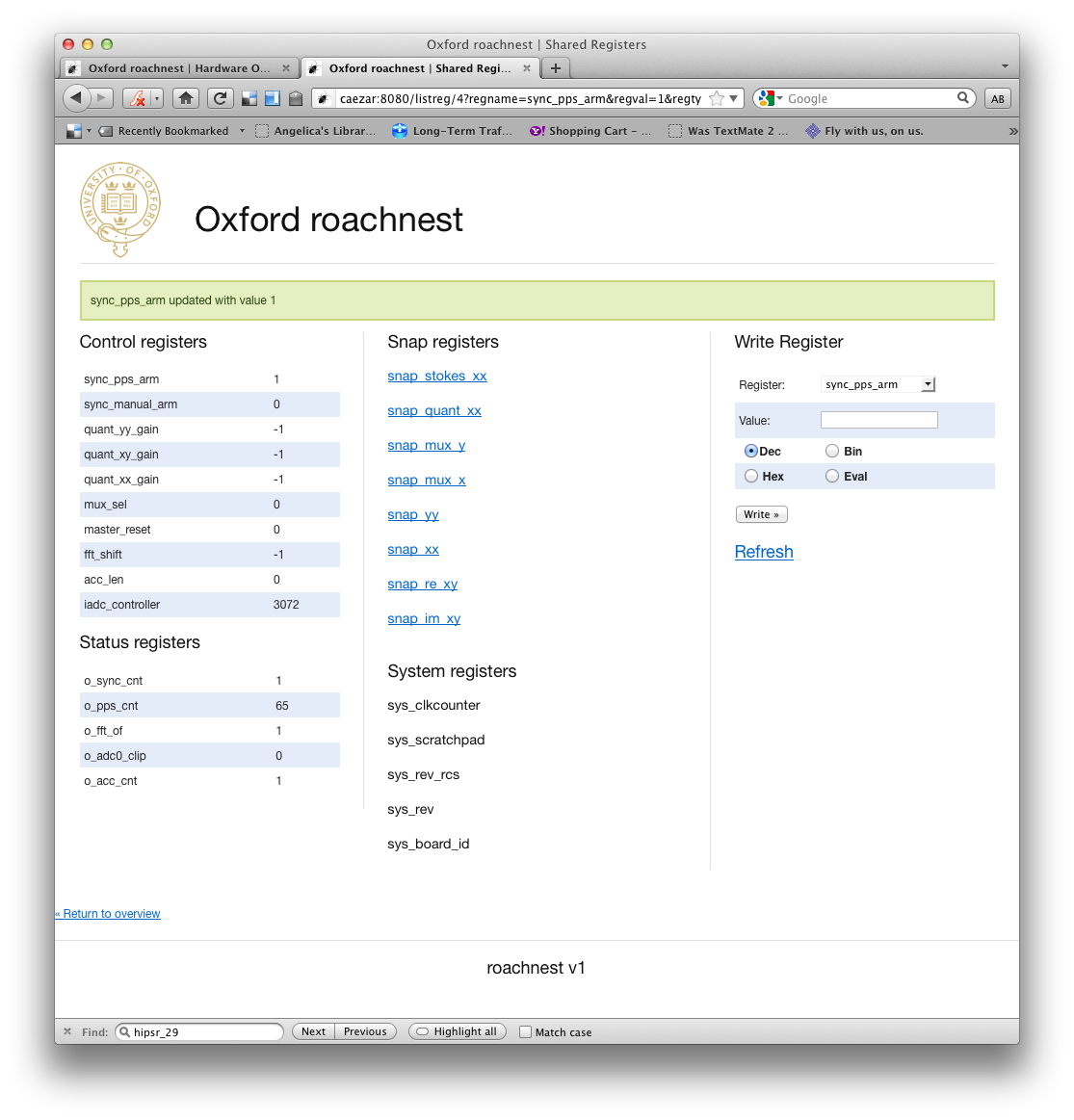
Screenshots¶
Getting Started¶
The first thing you’ll need to do is to satisy the dependencies. You’ll need:
Note that paste and lxml are optional: paste improves webserver performance by using threading, and lxml is for parsing configuration files – although these won’t appear until a future release!
After downloading the files, you should edit lib/config.py, and check that you’re happy with the configuration. Note that you can change the page titles and the logo in this file.
Next, assuming you’ve got the dependencies sorted, all you should need to do is run:
>> python roachnest.py [options]
This would start up a webserver on localhost:8080. The options available are:
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-p PORT, --port=PORT Select KATCP port. Default is 7147
-i HOSTIP, --hostip=HOSTIP
change host IP address to run server. Default is
localhost (127.0.0.1)
-P HOSTPORT, --hostport=HOSTPORT
change host port for server. Default is 8080
Once the webserver is up and running, open a browser up and surf over to localhost:8080, or if you’ve changed the IP address and port, type these in instead (eg. 192.168.126.6:8888). If you want the page to be viewable over a network, you’ll have to use the –hostip option and point this to the IP address of your ethernet card.
Module Listing¶
roachnest.py¶
Created by Danny Price on 2011-01-12.
Copyright (c) 2011 The University of Oxford. All rights reserved.
Roachnest is a browser based Graphical User Interface (GUI) for control of CASPER hardware. It facilitates basic monitor and control tasks, such as turning boards on and off via the XPORT, reprogramming the FPGA, reading and writing registers, and plotting the contents of shared BRAMS (snap blocks).
Roachnest also provides basic hardware management through a small sqlite database. Users can add notes, specify IP addresses, hostnames, and other basic information necessary to keep track of hardware specifics.
License: GNU GPL: http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/gpl.html
Warning: I strongly suggest that this is available only through an internal network and is not made accessible via the WWW. Use at your own risk.
- roachnest.create_db()¶
URL: /dbcreate
Creates a new database.
- roachnest.download(filename)¶
URL: /download/:filename
Forces download of static files.
- roachnest.hardware_add()¶
URL: /add
Add a new piece of kit to the database.
- roachnest.hardware_edit(id)¶
URL: /delete/:id
Delete a piece of kit from the database.
- roachnest.list_hardware()¶
URL: /
Index page. Lists all boards in the hardware database.
- roachnest.listbof(id)¶
URL: /listbof
Lists all bitstreams. Uses KATCP ?listbof command.
- roachnest.listreg(id)¶
URL: /listreg
Lists registers and applies basic sorting regex. Uses KATCP ?listdev command.
- roachnest.power_off(id)¶
URL: /poweroff/:id
Powers off a ROACH board using XPORT.
- roachnest.power_on(id)¶
URL: /poweron/:id
Powers up a ROACH board using XPORT.
- roachnest.progdev(id, bitstream)¶
URL: /progdev/:bitstream
Executes KATCP ?progdev command to program FPGA.
- roachnest.server_static(path)¶
URL: /files/:path#.+#
Returns static files (eg images, css, scripts, favicons).
- roachnest.snap32(id, snap_id, bytes, fmt, op)¶
URL: ajax_snap/:snap_id/bytes/:bytes/fmt/:fmt
AJAX request handler for /snap plotting page. Returns JSON data for the Flot javascript plotting library to plot.
- roachnest.view_hardware(id)¶
URL: /status/:id
Provides overview of a single piece of kit.
roachnest_helpers.py¶
Created by Danny Price on 2011-01-12.
Copyright (c) 2011 The University of Oxford. All rights reserved.
Helper functions and classes for roachnest.
- roachnest_helpers.bin2dec(binary)¶
return the decimal string representation of binary
Parameters : binary: binary string :
binary string to reinterpret as decimal
- roachnest_helpers.dbadd(hostname, MAC_address, IP_address, location, notes, serial, firmware, atype, XPORT_address, ZDOK0, ZDOK1)¶
Add a new piece of hardware to the database
Parameters : hostname: string :
Hostname of piece of hardware
MAC_address: string :
MAC address of KATCP interface
IP_address: string :
IP address of KATCP interface.
location: string :
Physical location of the hardware (eg Oxford DSP lab)
notes: string :
Any relevant notes that you may have
serial: string :
The serial number of the hardware.
firmware: :
Firmware revision information
atype: string :
What type of hardware is it? Options are generally ROACH, ROACH2, iBOB or BEE2
XPORT_address: string :
IP address of XPORT interface.
ZDOK0: string :
Notes about what is installed in ZDOK 0.
ZDOK1: string :
Notes about what is installed in ZDOK 1.
- roachnest_helpers.dbblank()¶
Returns a blank hardware dictionary.
Returns a BLANK python dictionary with the following entries: id, hostname, MAC_address, IP_address, location, notes, serial, firmware, type, XPORT_address, ZDOK0, ZDOK1, status, XPORT_status.
- roachnest_helpers.dbcreate()¶
Creates a new database.
Notes
This function should only be called once, for initial database setup.
- roachnest_helpers.dbdelete(id)¶
Deletes a piece of hardware from the database.
Parameters : id: int :
Primary key (ID number) of record
- roachnest_helpers.dbedit(id, hostname, MAC_address, IP_address, location, notes, serial, firmware, atype, XPORT_address, ZDOK0, ZDOK1)¶
Edit an exisiting piece of hardware in the database
Parameters : id: int :
Primary key (ID number) of record
hostname: string :
Hostname of piece of hardware
MAC_address: string :
MAC address of KATCP interface
IP_address: string :
IP address of KATCP interface.
location: string :
Physical location of the hardware (eg Oxford DSP lab)
notes: string :
Any relevant notes that you may have
serial: string :
The serial number of the hardware.
firmware: :
Firmware revision information
atype: string :
What type of hardware is it? Options are generally ROACH, ROACH2, iBOB or BEE2
XPORT_address: string :
IP address of XPORT interface.
ZDOK0: string :
Notes about what is installed in ZDOK 0.
ZDOK1: string :
Notes about what is installed in ZDOK 1.
- roachnest_helpers.dbget(id)¶
Retrieves a hardware record from the hardware database.
Parameters : id: integer :
primary key (ID number) of database entry
Notes
Queries database and returns a python dictionary with the following entries: id, hostname, MAC_address, IP_address, location, notes, serial, firmware, type, XPORT_address, ZDOK0, ZDOK1, status, XPORT_status.
- roachnest_helpers.dbgetall()¶
Retrieves all records from the database.
Notes
Retrieves all records from the database. Returns a list of python dictionaries, with name: value pairs that correspond to database columns. Each python dictionary contains the following entries: id, hostname, MAC_address, IP_address, location, notes, serial, firmware, type, XPORT_address, ZDOK0, ZDOK1, status, XPORT_status.
- roachnest_helpers.dec2bin(decimal)¶
return the binary string representation of a decimal Parameters ———- decimal: decimal string
decimal string to reinterpret as binary
- roachnest_helpers.dec2hex(n)¶
return the hexadecimal string representation of integer n
Parameters : n: hexadecimal string :
hexadecimal string to reinterpret as decimal
- roachnest_helpers.hex2dec(s)¶
return the integer value of a hexadecimal string s
Parameters : s: decimal string :
decimal string to reinterpret as hexadecimal
- roachnest_helpers.safe_eval(command)¶
A safer version of the eval() command, using ast.literal_eval TODO: make this more functional, at the moment it’s pretty useless.
Parameters : command: string :
command to evaluate (e.g. ‘2**10-1’).
- roachnest_helpers.writereg(fpga, name, value, base=10)¶
Writes a value to an FPGA register. Very similar to fpga.write_int, but you can specify the base (e.g. base 2 for binary)
Parameters : fpga: katcp_wrapper.FpgaClient object :
fpga client object (which roach board to communitcate with)
name: string :
register name
value: integer :
value to write to register
base: int :
base to write register. Default is 10 (decimal), but other bases may be used.
ping.py¶
Ping multiple hosts/ip addresses in parallel, using threading
Credits: Modified from script by Jose Porrua: http://www.joseporrua.com/2008/12/11/multi-threaded-ping-in-python However, this script didn’t work for me out of the box so I modified it to get it running.
- class ping.Host(ip)¶
Defines a host object.
Current attributes include: name, address and status.
- ping.execute(host)¶
Executes a ping command and sets the appropriate attribute.
Parameters : host: ping.Host :
A host object.
Notes
This is significantly different to Jose Porrua’s original script, which will not match ping requests on Mac OSX. TODO: Test this on Windows and modify if required.
- ping.ping(hostname)¶
Pings a single board
Parameters : hostname: string :
hostname or IP address of hardware to ping
- ping.pingHosts(hosts)¶
Creates and starts pinging threads.
Parameters : hosts: list [] :
A list of host objects.
- ping.printResults(hosts)¶
Prints a results: address status hostname
Parameters : hosts: list [] :
A list of ping.Host objects
xport.py¶
Created by Danny Price, 03 October 2011.
Based on roach_monitor.py at: https://casper.berkeley.edu/wiki/Roach_monitor_and_management_subsystem
This module allows for communication with the ROACH X-port. ROACH has an onboard, fully independent management subsystem that can be accessed through the Xport. The X-port system monitors voltages and temperatures and will shut down the board if these are out of specification. A log is kept of the shutdown cause, its value and time.
- class xport.Xport(ip, port)¶
Actel Fusion X-port class, for communicating with M&C
Methods
- clear_crashlog()¶
Reset crash log counter
- close()¶
Close xport socket connection
- connect()¶
Connect to xport socket
- flush()¶
Flush receive buffer
- get_board_time()¶
Check and retrieve board uptime. Returns board up time in seconds (int).
- get_channels()¶
Retrieves the voltage and temperatures of the PPC, V5, PSU, and Actel chips.
Returns a list of format: (channel name, channel state, channel min operational value, channel max operational val)
- get_fan_speeds()¶
Check and retrieve fan speeds. Returns a list of fan speeds
- get_id()¶
Return board ID and revision
- get_last_shutdown()¶
Check and retrieve reason for last shutdown. Returns reason as a string
- get_power_good()¶
Check and retrieve power good status of voltage regulators. Returns a list of power good signals.
- get_power_state()¶
Check and retrive board power state. Returns power state as a string
- get_serial()¶
Check and retrieve serial number. After first query the serial number is stored as class variable self.serial
- power_down()¶
Power down the ROACH
- power_up()¶
Power up the ROACH (Wake on LAN)
- read(addr)¶
Reads a 16bit value from the Fusion part through the Xport.
- toggle_config_h()¶
todo: Toggle PPC EEPROM boot (config H)
- toggle_power_on_reset()¶
todo: Toggle auto power-on after hard-reset.
- warm_rst()¶
Reset ROACH, but not Actel
- write(addr, value)¶
Writes a 16bit value to the Fusion part through the Xport.
- exception xport.xportError(msg)¶
A simple class for X-port error handling